Where this is not true, an arbitrageur might similarly short offer the pricey instrument, and utilize the proceeds to buy the correctly priced instrument, pocket the distinction, and then utilize payments created to service the instrument which he is brief. While principal payments are not exchanged in a rate of interest swap, presuming that these are received and paid at the end of the swap does not alter its worth. Therefore, from the viewpoint of the floating-rate payer, a swap is equivalent to a long position in a fixed-rate bond (i. e. getting fixed interest payments), and a brief position in a drifting rate note (i.
making floating interest payments): V s w a p = B f i x e d B f l o a t i n g \ displaystyle V _ \ mathrm swap =B _ \ mathrm fixed -B _ \ mathrm drifting \, From the point of view of the fixed-rate payer, the swap can be viewed as having the opposite positions. That is, V s w a p = B f l o a t i n g B f i x e d \ displaystyle V _ \ mathrm swap =B _ \ mathrm drifting -B _ \ mathrm repaired \, Similarly, currency swaps can be considered as having positions in bonds whose cash streams correspond to those in the swap.
One-month LIBOR is the rate used for 1-month deposits, 3-month LIBOR for 3 months deposits, etc. LIBOR rates are determined by trading in between banks and change continually as financial conditions alter. Similar to the prime rate of interest priced quote in the domestic market, LIBOR is a reference rate of interest in the international market. Saunders, A.; Cornett, M. (2006 ). Financial Institutions Management. Mc, Graw-Hill Irwin. [] Financial Market Organization Ontology Version 2, Annex D: Derivatives, EDM Council, Inc., Things Management Group, Inc., 2019 " What is a swap?". Investopedia. Obtained 14 October 2017. John C Hull, Options, Futures and Other Derivatives (6th edition), New Jersey: Prentice Hall, 2006, 149 " Comprehending Derivatives: Markets and Infrastructure - Federal Reserve Bank of Chicago".
org. Recovered 23 September 2017. Ross; Westerfield & Jordan (2010 ). Basics of Corporate Finance (9th ed.). Mc, Graw Hill. p. 746. " OTC derivatives stats at end-June 2017". www. bis.org. 2017-11-02. Recovered 2018-07-16. " Swaps Execution Facilities (SEFs)". U.S. Commodity Futures Trading Commission. Retrieved 9 December 2019. " Data Repositories". U.S. Commodity Futures Trading Commission. Retrieved 9 December 2019. " Bloomberg Launches Its Swap Data Repository". Bloomberg. Recovered 9 December 2019. " CME Swap Data Repository". " Exchange for Swaps". Eurex Exchange. Recovered 8 December 2019. Khwaja, Amir. " 2018 SEF Market Share Data". Clarus, FT. Retrieved 9 December 2019. " Intermediaries". U.S. Commodities Futures Trading Commission. Retrieved 8 December 2019.
( 1997 ). " Why companies utilize currency derivatives". Journal of Financing. 52 (4 ): 13231354. doi:10. 1111/j. 1540-6261. 1997. tb01112. x. Goswami, G.; Nam, J.; Shrikhande, M. (2004 ). "Why do international firms utilize currency swaps?: Theory and evidence". Journal of Multinational Financial Management. 14 (45 ): 315334. doi:10. 1016/j. mulfin. 2004. 03.003. What does leverage mean in finance. Li, H.; Mao, C. (2003 ). "Business use of rate of interest swaps: Theory and evidence". Journal of Banking & Financing. 27 (8 ): 15111538. doi:10. 1016/S0378 -4266( 02 )00275-3. " Financial Industry Service Ontology" Variation 2, Annex D: Derivatives, EDM Council, Inc., Things Management Group, Inc., 2019 " How Liquid Is https://www.healthcarebusinesstoday.com/how-to-keep-your-clients-happy/ the Inflation Swap Market?" Michael J. Fleming and John Sporn, 2013 Frank J.
Derivatives contracts can be divided into 2 basic households: 1. Contingent https://themazatlanpost.com/2020/11/07/4-ways-mexican-real-estate-agents-can-increase-their-productivity/ claims (e. g., options) 2. Forward claims, which consist of exchange-traded futures, forward contracts, and swaps A swap is an contract between two celebrations to exchange series of money flows for a set amount of time. Usually, at the time the agreement is started, at least among these series of capital is figured out by a random or unsure variable, such as a rate of interest, foreign exchange rate, equity rate, or commodity rate. Conceptually, one might view a swap as either a portfolio of forward contracts or as a long position in one bond combined with a brief position in another bond.
In finance, a swap is an acquired contract in which one party exchanges or swaps the worths or money flows of one asset for another. Of the 2 capital, one worth is fixed and one varies and based upon an index price, interest rate, or currency exchange rate. Swaps are customized contracts traded in the over the counter (OTC) market independently, versus choices and futures traded on a public exchange. The plain vanilla rates of interest and currency swaps are the 2 most common and fundamental types of swaps. Unlike a lot of standardized choices and futures contracts, swaps are not exchange-traded instruments.
The Of How To Find Number Of Shares Outstanding On Yahoo Finance
Companies and banks dominate the swaps market, with few (if any) people ever getting involved. Because swaps happen on the OTC market, there is constantly the risk of a counterparty defaulting on the swap. The first rates of interest swap took place between IBM and the World Bank in 1981. However, despite their relative youth, swaps have exploded in popularity. In 1987, the International Swaps and Derivatives Association reported that the swaps market had an overall notional worth of $865. 6 billion. By mid-2006, this figure went beyond $250 trillion, according to the Bank for International Settlements. That's more than 15 times the size of the U.S.
The most common and easiest swap is a plain vanilla interest rate swap. In this swap, Celebration A consents to pay Celebration B an established, fixed interest rate on a notional principal on specific dates for a specified time period. Simultaneously, Celebration B accepts pay based on a floating rates of interest to Celebration A on that exact same notional principal on the exact same defined dates for the exact same given period. In a plain vanilla swap, the two cash circulations are paid in the exact same currency - Which of the following was eliminated as a result of 2002 campaign finance reforms?. The specific payment dates are called settlement dates, and the times in between are called settlement periods.
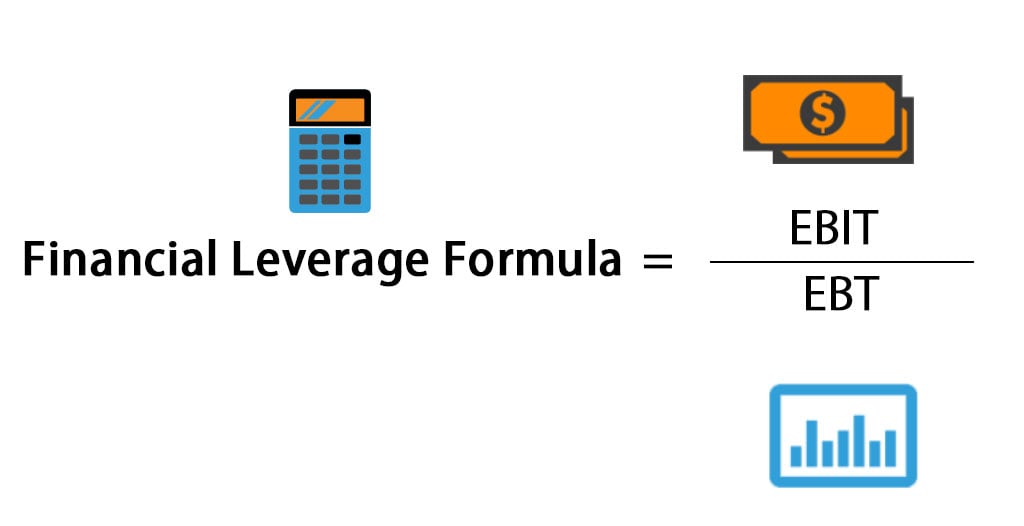
For instance, on Dec. 31, 2006, Business A and Company B participate in a five-year swap with the following terms: Company A pays Company B a quantity equivalent to 6% per year on a notional principal of $20 million. Company B pays Business A a quantity equivalent to one-year LIBOR + 1% per year on a notional principal of $20 million. LIBOR, or London Interbank Offered Rate, is the interest rate provided by London rely on deposits made by other banks in the Eurodollar markets. The market for interest rate swaps regularly (but not always) used LIBOR as the base for the floating rate until 2020.
For simpleness, let's assume the 2 celebrations exchange payments each year on December 31, starting in 2007 and concluding in 2011. At the end of 2007, Company A will pay Company B $1,200,000 ($ 20,000,000 * 6%). On Dec. 31, 2006, one-year LIBOR was 5. 33%; therefore, Company B will pay Company A $1,266,000 ($ 20,000,000 * (5. 33% + 1%)). In a plain vanilla interest rate swap, the floating rate is normally figured out at the start of the settlement period. Typically, swap agreements allow for payments to be netted against each other to avoid unnecessary payments. Here, Business B pays $66,000, and Business A pays nothing.